Introduction to Data VS Information
We frequently use the terms data vs information reciprocally however that is not the same term, and both have different meanings. The title of the article is data vs information because there is a significant amount of difference between the two. While you think it has a similar meaning, it doesn’t. The distinctions are subtle however very significant.
Also, to fully understand the difference between information and data, we really have to know what they mean by data vs information. Data refers to a number, symbol, character, or word. At the point when we don’t place them into context, individual bits of data seldom matter to us. On the other hand, information refers to data put into context. We utilize information in a huge way. For example, the computer can be an illustration of information. It utilizes scripts and programming applications for transforming data into information.
Independent of specific industries, data has turned into the main thrust that promotes the advancement of a variety of technologies and innovations. The term DATA is etymologically derived from the Latin word “datum,” which generally means “something given”.
Data is raw, unorganized, unanalyzed, uninterrupted, and unrelated and utilized in various contexts. For example, facts and statistics accumulated by researchers for their analysis can collectively be called data. Data basically lacks information and it moderately delivers itself to be meaningless except if given a purpose or direction to obtain its significance.
In any case, when that data is investigated, organized, and given composure or context to make it helpful, we then get information. The term INFORMATION is etymologically derived all the way back to Middle and Old French Roots, which meant “the act of informing,” generally used in the context of knowledge, guidance, and education. Generally, information is precise, filtered, and helpful.
In this article, we will delve into the differences between data and information or data vs information which are covered in a separate section of the article under data vs information. But before that, we will get an understanding of data and information separately. We will also cover all the frequently asked questions regarding data vs information. That will give a better understanding of the topic we will be discussing throughout the topic. The article will provide you with an insight into the world of data and information.
What is Data?

In order to get a greater understanding of data vs information, we must first know what data means. “Data is the New Oil.” Today data is everywhere in every field. Whether you are a data scientist, advertiser, businessman, researcher, data analyst, or you are in some other profession, you want to play or try different things with raw or organized data. Data has turned into a significant resource for all the organizations and data science jobs are on the uptrend.
Presently business runs on data, most organizations use data for their insights to make and launch campaigns, plan strategies, launch products, and services or evaluate various things. Today, as per a report, at least 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are produced each day.
Data is an assortment of details or data remaining in the form of either figure texts, symbols, descriptions, or simple observations of entities, events, or things with a possibility to be examined and drawn inferences. They are raw which requires rendering to obtain meaningful information.
Data has different forms like letters, numbers, pictures, or characters. Computer data for example is addressed as 0’s and 1’s – that can be deciphered to frame a fact or value. The measuring units of data are Nibble, Bits, kilobytes, Megabytes, Gigabytes, Bytes, Terabytes, Petabytes, etc. Data was previously put away in punched cards which were soon replaced by magnetic tapes followed by hard disk drives in data vs information.
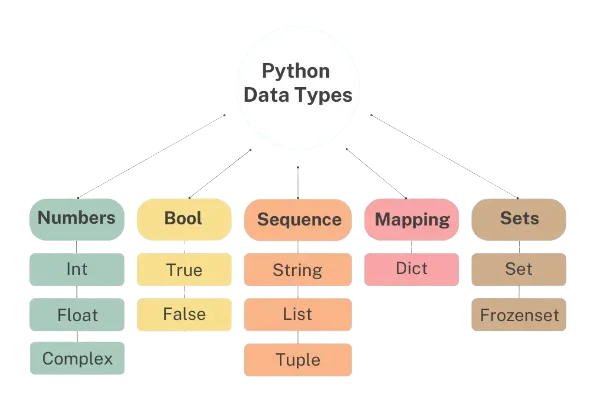
Types Of Data

There are two classes of data: Qualitative and Quantitative data, which are further classified into four types: nominal, ordinal, discrete, and Continuous. The classes of data along with the various types of data are depicted in the chart below
A. QUALITATIVE DATA
Qualitative or Categorical Data is data that can’t be measured or counted in the form of numbers. These types of data are sorted by category, not by number. That’s why it is also known as Categorical Data. These data consist of audio, images, symbols, or text.
The gender of a person, i.e., male, female, or others, is qualitative data. Qualitative data tells about the perception of people. This data helps market researchers understand the customers’ tastes and then design their ideas and strategies accordingly.
TYPES OF QUALITATIVE DATA- The qualitative data is further divided into two types in data vs information:
- NOMINAL DATA – Nominal Data labels variables without any order or quantitative value. The color of hair can be considered nominal data, as one color can’t be compared with another color. The name “nominal” comes from the Latin name “nomen,” which means “name.” With the help of nominal data, we can’t do any numerical tasks or give any order to sort the data. These data don’t have any meaningful order; their values are distributed into distinct categories.
- ORDINAL DATA – Ordinal data have natural ordering where a number is present in some kind of order by their position on the scale. These data are used for observation like customer satisfaction, happiness, etc., but we can’t do any arithmetical tasks. The ordinal data is qualitative data for which their values have some kind of relative position.
These kinds of data can be considered as “in-between” the qualitative data and quantitative data. The ordinal data only shows the sequences and cannot use for statistical analysis. Compared to the nominal data, ordinal data have some kind of order that is not present in nominal data.
B. QUANTITATIVE DATA
Quantitative data can be expressed in numerical values, which makes it countable and includes statistical data analysis. These kinds of data are also known as Numerical data. It answers the questions like, “how much,” “how many,” and “how often.”
For example, the price of a phone, the computer’s ram, the height or weight of a person, etc., falls under the quantitative data. Quantitative data can be used for statistical manipulation. These data can be represented on a wide variety of graphs and charts such as bar graphs, histograms, scatter plots, boxplots, pie charts, line graphs, etc.
TYPES OF QUANTITATIVE DATA- The quantitative data is further divided into two types:
- DISCRETE DATA- The term discrete means distinct or separate. The discrete data contain the values that fall under integers or whole numbers. The total number of students in a class is an example of discrete data. These data can’t be broken into decimal or fraction values. The discrete data are countable and have finite values; their subdivision is not possible. These data are represented mainly by a bar graph, number line, or frequency table.
- CONTINUOUS DATA- Continuous data are in the form of fractional numbers. It can be the version of an android phone, the height of a person, the length of an object, etc. Continuous data represents information that can be divided into smaller levels. The continuous variable can ta
ke any value within a range. The key difference between discrete and continuous data is that discrete data contains the integer or whole number. Still, continuous data stores the fractional numbers to record different types of data such as temperature, height, width, time, speed, etc.
What is Information?

In order to get a greater understanding of data vs information, we must first know what information means. Information is data collated to derive meaningful inferences according to its contextual requirement. Information is structured, processed, and presented with assigned meaning that improves the reliability of the data acquired. Information also ensures that there remains no uncertainty or undesirable. In essence, Information exists to systematize relevant and timely data to inform or develop ideas. Unlike data, information is critical since it processes data through purposeful intelligence to interpret or predict or explain.
The form of data in a processed, organized, specific and structured manner is known as information. It is derived from the Latin term ‘informare’ which means ‘give form to’. Moreover, it gives meaning to the data and also enhances its reliability. Most importantly, information helps in guaranteeing understanding and also reduces any kind of uncertainty. In other words, when we transform data into information, it becomes free from all the unnecessary details or immaterial things. Thus, you see how raw data does not give meaning like information. We have to refine and clean it with the help of purposeful intelligence to turn it into information.
Types of Information
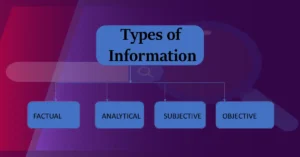
There are 4 types of information which are explained below:
- FACTUAL INFORMATION – Factual information is information that solely deals with facts. It is short and non-explanatory. The best place to find factual information is in reference books such as encyclopedias and almanacs.
- ANALYTICAL INFORMATION-Analytical information is the interpretation of factual information. What does the factual information mean? What does it imply? This is the type of information that researchers generate in their studies. Analytical information is mostly found in books and journals.
- SUBJECTIVE INFORMATION-Subjective information is information from only one point of view. Opinions are subjective. You can find subjective information almost anywhere factual information isn’t. It is in books, journals, websites, and book reviews.
- OBJECTIVE INFORMATION- Objective information is information that is understood from multiple viewpoints and presents all sides of an argument. Reference books are a good place to find objective information. Newspapers that have balanced and fair reporting are also objectives. Opposing Viewpoints and Facts on File are both great objective databases.
Data vs Information

Data vs Information is one of the most debatable subjects in today’s times. Data contains raw figures and facts. Information unlike data provides insights analyzed through the data collected. Information can’t exist without data but data doesn’t rely on the information. Data, as an input, goes through a filtration process followed by a meaningful organization to generate output or information.
Data doesn’t deliver into specifics since there is rarely any relevance scattered amongst heaps of data unless processed. Information is particular with a correlation to the inferences derived. Data doesn’t harbor any real meaning whereas information exists to provide insights and meaning. The following table depicts the difference between data and information:
DATA VS INFORMATION CHART
|
BASIS OF COMPARISON |
DATA |
INFORMATION |
|
MEANING |
It refers to raw facts that one gathers about something and are bare and random.Qualitative/ Quantitative variables that present themselves with the potential to be developed into ideas or analytical conclusions. |
Information is facts regarding something put into a context that is refined through processing. Data that is structured and collated to further its meaning and contextual usefulness. |
|
NATURE |
They are text, numbers, symbols, and more. |
It is refined data. |
|
FORM |
Unorganized: Data doesn’t serve any purpose unless given to. |
Organized: Data when interpreted and assigned with some meaning derived out of it gives information. |
|
USES |
Data alone doesn’t pertain to the qualities to help derive decisions. Data acquired by researchers might become useless if they have no analytical inferences to make. It may or may not come in use. |
The information contains analytical coherence to help derive a decision. Information adds value and usefulness to researchers since they are readily available. Information always comes in use. |
|
CHARACTERISTIC |
Data does not depend on information. |
We cannot process information without data. |
|
BASIS |
Data is based on records plus observations. |
Information is based on analysis. |
|
FEATURES |
Data is raw and doesn’t contain any meaning unless analyzed. |
Information is data collated and produced to further a logical meaning. |
|
UNIT |
Data is measured in bits and bytes. |
Information is mostly measured in units like quantity, time et al. |
|
INTERDEPENDENCE |
Data doesn’t depend on information. |
Information can’t exist without data. |
|
REPRESENTATION |
Data is structured either in graphs, data trees, flowcharts, or tables. |
Information is represented as ideas, thoughts, and languages after collating the data acquired. |
Data vs Information in Computers
Let us understand data vs information in computers. The terms data and information are at times mistakenly utilized in place of each other when truly there is a clear distinction between the two. The major and principal difference between information and data is the significance and worth ascribed to each term. Data is aimless in itself, yet once handled and interpreted, it becomes information that is loaded up with importance.
Another clear distinction between data and information in computers is that Data are simply facts or figures they are bits of information, but not information itself. Data and information in computers are measured in bits and bytes. PCs, with their huge number of circuits and switches, utilize the binary system to represent on and off or true and false, using bits and bytes.
To put this in perspective and according to statistics from TechJury, by 2020, every person will generate 1.7 megabytes of data in just a second which is 1,048,576 bytes. By 2025, it’s assessed that 463 exabytes of data will be made around the world, consistently. In the world of computer sciences, information is much
more valuable than data but it wouldn’t be wrong if we quote that without data there is no information possible.
Data vs Information in Statistics
Let us understand data vs information in statistics. Data in statistics means the use of figures and facts to prepare statistics. It may consist of one entry or a collection of different values. The information in statistics describes values and context together, resulting in something meaningful that would help to draw a conclusion. While data in statistics is raw and unorganized, information is organized. Data points are individual and sometimes unrelated.
Information maps out that data to provide a big-picture view of how it all fits together. Often the terms data and statistics are interchangeably used just like information and data. In other words, some computation has taken place that provides some understanding of what the data means and is often regarded as statistics. Statistics are often presented in the form of a table, chart, or graph.
Both statistics and data are frequently used in scholarly research. Statistics are often reported by government agencies – for example, unemployment statistics or educational literacy statistics. These statistics are prepared with the help of data and information. At first, data is gathered with is raw and meaningless which is then processed and presented and it becomes information, now when the information is presented in form of a conclusive result it is called statistics. Often these types of statistics are referred to as ‘statistical data.
For example in a given area survey is conducted on how many people are unemployed. So the data collected is raw now when the data is listed and categorized according to age, area, etc. it becomes information as it is now meaningful and organized. Now, this is pictorially represented and it becomes statistics of a particular area.
Data vs Information in Business and HealthCare
Let us understand data vs information when it comes to the business and healthcare industry. Data means laying out information followed by strategic success in the business world. Without data, advances in business won’t exist. A decent business remains on market analysis, assembled around data analysis that sieves raw data for significant insights. So, with information exists a more noteworthy scope for deriving progress in most business ventures.
From data to information and from that information to business intelligence, each business today depends on the data produced. Business organizations are exploiting this cycle to make a distinction in their market approach. Business Information like its different sections in the data business has several forms i.e., News, Credit and Financial Information, Market Research, IT Research, and Industry Analysis. They can additionally be arranged into registries, periodicals, details, stats, government data, guides, handbooks, chronicles, and indexes.
The Internet has made it generally easier for publishers to convey business information, particularly with membership models that convey content to their client base. Market Stats doesn’t simply come from a direct source of data, it is fairly a thorough interaction where examiners separate the good and useful data – which is the foundation for any business technique.
Data and Information make it possible both to distinguish illnesses of an individual and to foresee the condition of the health of the entire society. Consequently, carrying out Big Data in medical services is the way to create preventive measures and save lives. Healthcare information and data systems help assemble, incorporate and break down relevant health data to assist with managing everyone’s wellbeing and diminish medical care costs.
Data Science vs Information Technology: Which is better?

We are covering is data vs information is correlated with data science and information technology. The principal purpose of Data Science is to find patterns within data. It uses various statistical techniques to analyze and draw insights from the data. From data extraction, wrangling, and pre-processing, a Data Scientist must scrutinize the data thoroughly. Whereas, Information technology helps to build and grow the commerce and business sector and generate the maximum possible output. The time taken by different sectors to generate business is now minimized with advancements in Information technology. It provides electronic security, storage, and efficient communication.
Data science is used in business functions such as strategy formation, decision making, and operational processes. It touches on practices such as artificial intelligence, analytics, predictive analytics, and algorithm design. The discovery of knowledge and actionable information in data. Data science is an interdisciplinary field about scientific methods, processes, and systems to extract knowledge or insights from data in various forms, either structured or unstructured.
Information technology (IT) is the use of any computers, storage, networking, and other physical devices, infrastructure, and processes to create, process, store, secure, and exchange all forms of electronic data. The commercial use of IT encompasses both computer technology and telephony. It is the development, maintenance, and use of computer software, systems, and networks. It includes their use for the processing and distribution of data in data vs information. Data means information, facts, statistics, etc.
Data vs Information both have their benefits, it’s always upon the seeker to choose which one is better according to their preferences and needs.
Also Read: Click Here to know about Data Science Artificial Intelligence
CONCLUSION
As of now we have come across all the information about data vs information let’s conclude by saying these terms through seem to be similar are very different in their meaning. Data means laying out information followed by strategic achievements. Thus in data vs information, without data, the following advances won’t exist in data vs information. A decent business remains on market examination, accumulated around data analysis that the raw data for significant insights. From data to information and from information to business intelligence, every business relies on the data generated. Businesses are taking advantage of this process to create a difference in their market approach.
Business Information like its other segments in the information industry has several forms i.e., News, Credit & Financial Information, Market Research, IT Research, and Industry Analysis. They can further be categorized into directories, periodicals, stats, government information, guides, handbooks, almanacs, and directories. The Internet has made it relatively easier for publishers to deliver business information, especially with subscription models that deliver content to their user base. Market research doesn’t just stem from a linear source of data, it is rather an exhaustive process where analysts separate the good data – which is the cornerstone of any business strategy.
Now, you will have business information systems that are designed to help organizations make important decisions via objective attainment. This system uses the resources provided in most IT Infrastructures to satiate the needs of variant e
ntities existing inside a business enterprise.
For any research process to start, we need to collect data beforehand in data vs information. Thus, you see how it plays an essential role in statistical analysis. In other words, data denotes the facts or statistics which a researcher gathers for the purpose of analysis in their original form. Hence, you see how data is an unsystematic fact or detail concerning something or someone. They divide further into qualitative and quantitative data plus internal and external data respectively. After the processing and transforming of data are done in a way to make it useful, we gain information. It is a systematic and filtered form of data that is very useful.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between data and information?
Data vs Information, Data contains raw figures and facts. Information unlike data provides insights analyzed through the data collected. In data vs information, Information can’t exist without data but data doesn’t rely on the information. Data, as an input, goes through a filtration process followed by a meaningful organization to generate output or information.
At the point when raw data is handled, deciphered, coordinated, organized, or presented to make it significant or helpful, then it is called information. For instance, a list of random dates is raw data that is meaningless without proper information that makes the dates relevant. This is one of the most asked data vs information questions.
2. What are 3 differences between data and information?
The three differences between data and information are given in the table below:
DATA VS INFORMATION
|
DATA |
INFORMATION |
|
It refers to raw facts that one gathers about something and are bare and random.Qualitative/ Quantitative variables that present themselves with the potential to be developed into ideas or analytical conclusions. |
Information is facts regarding something put into a context that is refined through processing. Data that is structured and collated to further its meaning and contextual usefulness. |
|
Data doesn’t depend on information. |
Information can’t exist without data. |
|
Data is based on records plus observations. |
Information is based on analysis. |
The example of data in data vs information is given below:
- List of Weights, Prices, Costs, Numbers of items sold, Employee Names, Product Names, Addresses, Tax Codes, Registration Marks, etc. Images, sounds, Multimedia, and Animated data.
These examples will help you understand the difference more easily, which we had already covered in the data vs information article above.
4. What are the 5 examples of information?
5 examples of information in data vs information are given below:
- FACTUAL INFORMATION: For your information, water accounts for about 60% of an adult’s weight.
- ANALYTICAL INFORMATION: Based on crash statistics, Arkansas State Police designated the road as dangerous.
- SUBJECTIVE INFORMATION: I hate Rajasthans’ hot, humid summers!
- OBJECTIVE INFORMATION: While many people don’t like Jaipur summers, some look forward to the season so they can travel.
- Mount Everest is the highest mountain peak in the world.
These examples will help you understand the difference more easily, which we had covered in the data vs information article above.
5. What is the difference and similarity between data and information?
The difference and similarity in data vs information is given in the table below:
DATA VS INFORMATION
|
DATA |
INFORMATION |
|
|
DIFFERENCE |
It refers to raw facts that one gathers about something and are bare and random.Qualitative/ Quantitative variables that present themselves with the potential to be developed into ideas or analytical conclusions. |
Information is facts regarding something put into a context that is refined through processing. Data that is structured and collated to further its meaning and contextual usefulness. |
|
SIMILARITY |
Data is a type of knowledge. |
Information is also a type of knowledge. |
6. What are the information and examples?
In data vs information the information is facts regarding something put into a context that is refined through processing. Data that is structured and collated to further its meaning and contextual usefulness. The examples are given below:
- FACTUAL INFORMATION: For your information, water accounts for about 60% of an adult’s weight.
- ANALYTICAL INFORMATION: Based on crash statistics, Arkansas State Police designated the road as dangerous.
- SUBJECTIVE INFORMATION: I hate Rajasthans’ hot, humid summers!
- OBJECTIVE INFORMATION: While many people don’t like Jaipur summers, some look forward to the season so they can travel.
These examples will help you understand the difference more easily, which we had already covered in the data vs information article above.
7. Which is more useful data or information?
This is one of the most asked data vs information questions. According to me, Information is a more reliable form of knowledge in comparison to data.
In data vs information the data is raw, unorganized pieces of knowledge whereas information is more comprehensive and precise data. So for anyone that is doing his research gradually the preference is information and not data.
In data vs information, the data refers to raw facts that one gathers about something and are bare and random. Data is Qualitative or Quantitative variables that present themselves with the potential to be developed into ideas or analytical conclusions or important pieces of information.
Data contains raw figures and facts. Here data vs information, Data as an input, goes through a filtration process followed by a meaningful organization to generate output or information. It is important to understand the concept of data to get a clear picture of data vs information.
9. What are the types of information?
The four types of information in data vs information are given below:
- FACTUAL INFORMATION – Factual information is information that solely deals with facts. It is short and non-explanatory.
- ANALYTICAL INFORMATION-Analytical information is the interpretation of factual information.
- SUBJECTIVE INFORMATION-Subjective information is information from only one point of view. Opinions are subjective.
- OBJECTIVE INFORMATION- Objective information is information that is understood from multiple viewpoints and presents all sides of an argument. Reference books are a good place to find objective information.
These types will help you understand the difference more easily, which we had already covered in the data vs information article above.
10. What is data from Wikipedia?
Data according to Wikipedia data vs inforamtion means:
Data (US: /ˈdætə/; UK: /ˈdeɪtə/) are individual facts, statistics, or items of information, often numeric.[1] In a more technical sense, data are a set of values of qualitative or quantitative variables about one or more persons or objects, while a datum (singular of data) is a single value of a single variable.
It is important to understand the concept of data to get a clear picture of data vs information.